Kelvin Boiling Point Of Water: The Science Behind The Heat
Hey there, science enthusiasts! Let's dive straight into the fascinating world of thermodynamics. Today, we're unraveling the mystery behind kelvin boiling point of water. If you're wondering why this topic is so crucial, it’s because understanding the boiling point in kelvin plays a pivotal role in various scientific applications, from cooking to industrial processes. So, grab your lab goggles and let’s get started!
Now, before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let me ask you a question. Have you ever thought about why water boils at 100 degrees Celsius but not in kelvin? Or why scientists prefer using kelvin over other temperature scales in their research? These are the questions we’ll answer as we explore the boiling point of water in kelvin. Stick around, because it’s going to be an exciting ride!
So, why does the boiling point matter? Well, it’s not just about heating water for your morning coffee. The boiling point in kelvin is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry. Understanding it helps us comprehend how substances behave under different conditions. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just someone curious about the world around you, this article is for you!
- Sage Stallone The Life And Legacy Of A Talented Actor
- Michael Keatons Son A Glimpse Into The Life Of Sean Douglas
Understanding the Kelvin Scale
Alright, let’s start with the basics. The kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale used in science. Unlike Celsius or Fahrenheit, kelvin doesn’t have negative numbers. It starts at absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion stops. This makes kelvin the perfect scale for scientific calculations and measurements.
Now, here’s a fun fact: the kelvin scale is named after Lord Kelvin, a brilliant physicist who made significant contributions to thermodynamics. So, whenever you’re working with kelvin, you’re honoring the legacy of a scientific genius. Pretty cool, right?
Why Use Kelvin Over Other Scales?
When it comes to measuring temperature, kelvin has a few advantages. First, it eliminates the need for negative numbers, which simplifies calculations. Second, it’s universally accepted in scientific communities, ensuring consistency across experiments and studies. Finally, kelvin aligns perfectly with the laws of thermodynamics, making it indispensable in fields like physics and chemistry.
- Who Is Benson Boones Girlfriend Exploring The Young Stars Love Life
- Anant Ambani A Comprehensive Insight Into His Life And Achievements
- Kelvin simplifies scientific calculations.
- It’s universally accepted in the scientific community.
- Kelvin aligns with the laws of thermodynamics.
The Boiling Point of Water in Kelvin
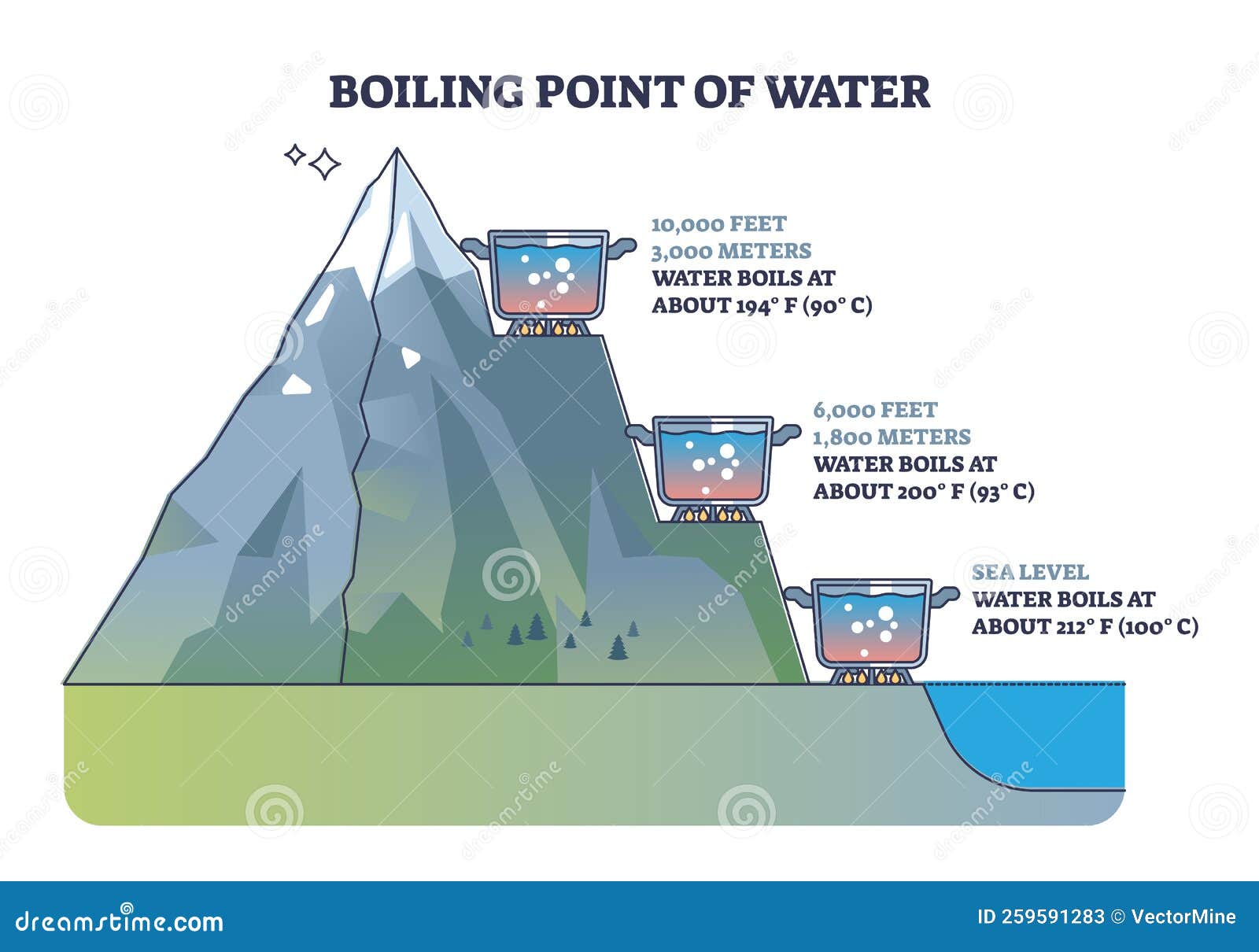
Alright, let’s talk about the star of our show: the boiling point of water in kelvin. At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 373.15 kelvin. Why 373.15? Well, it’s because kelvin is directly related to Celsius. To convert Celsius to kelvin, you simply add 273.15. So, 100 degrees Celsius becomes 373.15 kelvin. Easy peasy, right?
But here’s where things get interesting. The boiling point of water can change depending on the atmospheric pressure. For example, at higher altitudes, where the pressure is lower, water boils at a lower temperature. This means the boiling point in kelvin will also decrease. Fascinating, isn’t it?
Factors Affecting the Boiling Point
Several factors can influence the boiling point of water in kelvin. Let’s take a look at some of them:
- Atmospheric Pressure: As mentioned earlier, lower pressure leads to a lower boiling point.
- Impurities: Adding substances like salt or sugar to water can increase its boiling point.
- Container Material: Believe it or not, the material of the container can also affect the boiling point slightly.
Practical Applications of Kelvin Boiling Point
So, why do we care about the boiling point of water in kelvin? Well, it has numerous practical applications. For instance, in cooking, understanding the boiling point helps chefs achieve the perfect texture for their dishes. In industry, precise temperature control is crucial for processes like distillation and sterilization. And in scientific research, the boiling point in kelvin is a key parameter in experiments involving phase changes.
Let’s not forget about space exploration. When designing equipment for space missions, engineers need to consider how materials behave at extreme temperatures. The boiling point in kelvin provides valuable insights into these behaviors.
Boiling Point in Everyday Life
Even in our daily lives, the boiling point of water in kelvin plays a role. Think about boiling water for tea or pasta. Knowing the boiling point helps us determine how long to cook our food. And let’s not forget about altitude adjustments when cooking at higher elevations. It’s all about understanding the science behind the heat!
History of the Kelvin Scale
Now, let’s take a trip back in time to explore the history of the kelvin scale. It all started with Lord Kelvin, whose groundbreaking work in thermodynamics laid the foundation for modern science. In the mid-19th century, he proposed the idea of an absolute temperature scale, which eventually became the kelvin scale we know today.
Lord Kelvin’s contributions didn’t stop there. He also developed the second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy, or disorder, always increases in a closed system. This law is fundamental to our understanding of the universe and has far-reaching implications in fields like engineering and biology.
Key Milestones in Kelvin Development
Here are some key milestones in the development of the kelvin scale:
- 1848: Lord Kelvin proposes the concept of absolute zero.
- 1864: The kelvin scale is officially adopted by the scientific community.
- 1954: The kelvin is redefined based on the triple point of water, making it even more precise.
Comparing Kelvin with Other Scales
While kelvin is the preferred scale in science, it’s helpful to understand how it compares to other temperature scales. Let’s take a look at the differences:
- Celsius: Kelvin and Celsius are closely related, with a simple conversion formula.
- Fahrenheit: Fahrenheit is more commonly used in everyday life, especially in the United States.
- Rankine: Similar to kelvin, but used primarily in engineering.
Each scale has its own strengths and weaknesses, but kelvin stands out for its precision and universality in scientific research.
Conversion Formulas
Here are the formulas for converting between kelvin and other scales:
- Kelvin to Celsius: K = °C + 273.15
- Kelvin to Fahrenheit: K = (°F + 459.67) × 5/9
- Kelvin to Rankine: K = °R × 5/9
Modern Uses of Kelvin Boiling Point
In today’s world, the boiling point of water in kelvin is more relevant than ever. From climate research to medical advancements, understanding temperature plays a crucial role in shaping our future. For example, scientists use kelvin to study global warming and its impact on our planet. By analyzing temperature changes, they can predict future trends and develop strategies to mitigate their effects.
In the medical field, precise temperature control is essential for procedures like cryopreservation and hyperthermia therapy. The boiling point in kelvin provides the necessary data for these applications, ensuring safety and efficacy.
Future Developments
As technology advances, the importance of kelvin in scientific research will only grow. New discoveries in quantum mechanics and nanotechnology rely heavily on precise temperature measurements. The boiling point of water in kelvin will continue to be a fundamental concept in these fields, driving innovation and progress.
Conclusion
And there you have it, folks! We’ve explored the kelvin boiling point of water and uncovered its significance in science and everyday life. From its origins in the work of Lord Kelvin to its modern applications, the kelvin scale has proven to be an invaluable tool for researchers and enthusiasts alike.
So, what’s next? If you found this article helpful, feel free to share it with your friends and family. And don’t forget to check out our other articles for more fascinating insights into the world of science. Together, let’s keep learning and growing!
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Kelvin Scale
- The Boiling Point of Water in Kelvin
- Practical Applications of Kelvin Boiling Point
- History of the Kelvin Scale
- Comparing Kelvin with Other Scales
- Modern Uses of Kelvin Boiling Point
- Val Kilmer 2024 A Look Into The Iconic Actors Journey And Future Projects
- Sage Stallone The Life And Legacy Of A Talented Actor

Melting And Boiling Point Of Water In Kelvin at Angelina Otto blog
Boiling Point of Water in Different Altitude Meter Levels Outline

SR0153 Boiling Point